Gnats, those tiny, persistent insects that seem to materialize out of thin air, can be an annoyance to humans. While their size might make them seem harmless, the question lingers: Can gnats actually hurt humans? Following the world of gnats, examining their behaviors, potential threats, and ways to mitigate their impact.
Table of Contents
The Anatomy of Gnats
To understand the impact gnats can have on humans, it’s essential to first grasp their anatomy and behavior. Gnats belong to the fly family, encompassing a variety of species such as fruit flies, fungus gnats, and biting midges. These insects are characterized by their small size, ranging from 1 to 4 millimeters, and their distinctive long, delicate legs.
Types of Gnats
Fruit Flies: Often found hovering around ripened fruits, these gnats can become unwelcome kitchen guests.
Fungus Gnats: Commonly seen near houseplants, these gnats thrive in damp environments, laying their eggs in the soil.
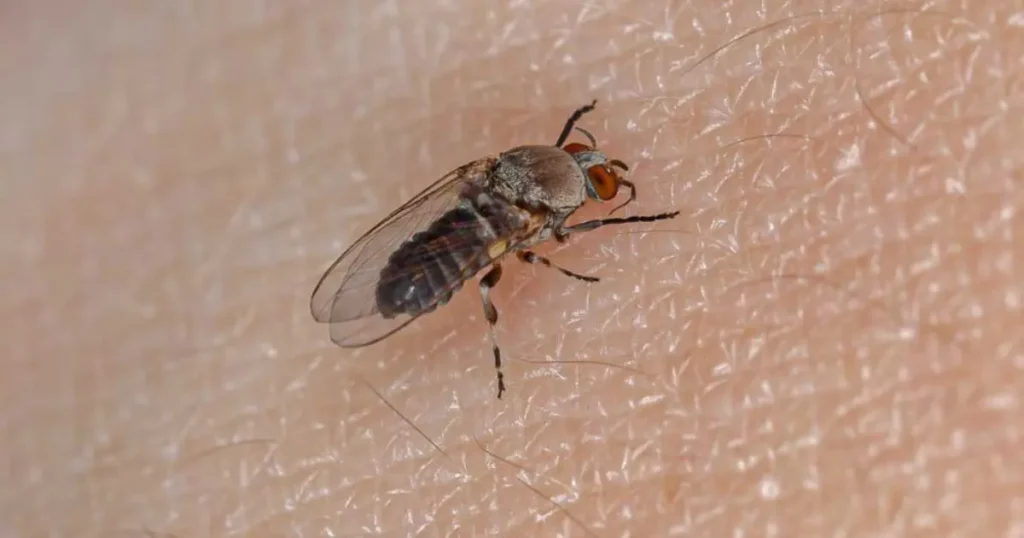
Biting Midges: Unlike their non-biting counterparts, these gnats can cause discomfort with their bites, resembling tiny mosquitoes.
The Harmless Buzz: Gnats and Humans
Anecdotal Encounters
Imagine a warm summer evening, a perfect sunset, and a serene outdoor gathering. Suddenly, the peace is disrupted by the persistent buzz of gnats. Many of us have experienced such scenarios, swatting at these tiny insects while questioning their potential harm.
In truth, the vast majority of gnats are more of a nuisance than a direct threat to humans. Their presence can be irritating, especially in large numbers, but they rarely cause significant harm.
Bites and Irritation
While most gnats are harmless, some, like biting midges, can deliver irritating bites. These bites, though not dangerous, can cause itching and discomfort. It’s essential to differentiate between the annoyance of a gnat bite and the potential health risks associated with other insect bites.
Unraveling the Myth: Gnats and Disease
Clarifying Misconceptions
One common misconception is that gnats are carriers of diseases. Unlike mosquitoes, which are notorious for transmitting illnesses like malaria and dengue fever, most gnats do not pose a significant disease risk to humans.
It’s crucial to stay informed about the specific types of gnats prevalent in your area to assess any potential health concerns accurately.
Strategies for Gnat Control
Now that we’ve explored the nuances of gnats and their interactions with humans, let’s delve into effective strategies for gnat control. Whether you’re dealing with fruit flies in the kitchen or fungus gnats in your houseplants, these steps can help you manage the situation.
1. Identify the Culprit: Different gnats require different approaches. Identifying the specific type infesting your space is the first step in effective control.
2. Remove Breeding Sites: Gnats often lay their eggs in damp environments. Eliminate breeding grounds by addressing areas with excess moisture, such as overwatered plants or clogged drains.
3. Natural Repellents: Consider using natural repellents like essential oils to deter gnats. Citronella, eucalyptus, and peppermint oils are known for their insect-repelling properties.
4. Insect Traps: Utilize gnat traps to capture adult insects and break the breeding cycle. These traps can be strategically placed in areas where gnats are most problematic.
5. Maintain Cleanliness: Keep living spaces clean and free of food debris, which can attract certain types of gnats.
6. Screens and Nets: Use screens on windows and doors to prevent gnats from entering your home. Nets can be particularly useful in outdoor settings.
7. Chemical Solutions: In severe infestations, consider chemical solutions specifically designed for gnat control. However, use them cautiously and follow safety guidelines.
The Power of Prevention
As the saying goes, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of gnat infestations and the associated inconveniences.
Regular Inspection: Conduct regular inspections of potential breeding sites, such as potted plants and drainage areas, to catch and address issues early.
Proper Waste Disposal: Dispose of organic waste promptly, as decaying matter can attract gnats. Composting bins can be sealed to prevent these insects from breeding.
Adequate Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in indoor spaces to discourage the buildup of humidity, which can attract certain types of gnats.
Conclusion: Living Harmoniously with Gnats
While gnats may be a persistent annoyance, they generally pose minimal harm to humans. Understanding their behavior, differentiating between species, and implementing effective control measures can create a harmonious coexistence.
Next time you find yourself swatting at a gnat, remember that it’s likely just a momentary inconvenience rather than a genuine threat. By taking proactive steps and incorporating preventive measures, you can enjoy a gnat-free environment and appreciate the outdoors without the buzzing distractions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to gnats and their interaction with humans:
1. Are gnats dangerous to humans?
In general, most gnats are not dangerous to humans. They are more of a nuisance than a direct threat. While some species can deliver irritating bites, these bites are typically not harmful and may cause only minor discomfort.
2. Can gnats transmit diseases to humans?
Unlike mosquitoes, which are known disease vectors, most gnats do not transmit diseases to humans. It’s essential to differentiate between various insect species and their potential health risks.
3. How can I identify the type of gnats infesting my space?
Identifying the specific type of gnats is crucial for effective control. You can observe their behavior, appearance, and the environments they are found in. Additionally, online resources and pest control experts can assist in proper identification.
4. What are some natural remedies for gnat control?
Natural remedies include using essential oils with insect-repelling properties, such as citronella, eucalyptus, and peppermint. Other methods include maintaining cleanliness, removing breeding sites, and using gnat traps strategically placed in problem areas.
5. When should I consider using chemical solutions for gnat control?
Chemical solutions should be considered in severe gnat infestations when natural and preventive measures are not effective. It’s crucial to use these solutions cautiously, following safety guidelines provided by the products, and consider consulting with pest control professionals if needed.